KORE's trusted certification process provides support in understanding the scope of your device certification, identifies required certifications based on product capabilities, operating regions and regulatory requirements and oversees the implementation to ensure your devices meet the standards of operation.

Certified devices have gone through the process to authenticate their connectivity capabilities against specific requirements. These certification requirements for operation are put in place by industry, local regulatory and network providers based on the operating region.

IoT devices that do not meet certification regulations can cause interference for other nearby devices and networks, potentially impacting network availability and performance while also posing a security liability. The certification process ensures that devices maintain a safe and reliable connection that does not compromise the surrounding global wireless networks.

Device Certification can be time consuming and costly, especially if a failed certification results in your company having to redesign major parts of the product. KORE's experts initiate and complete the certification process on your behalf to expedite completion and avoid pitfalls by creating an effective plan to meet the regulatory requirements with the lowest investment expense.
Many countries have regulations that are created by their government or by other lawmaking bodies, such as the FCC in the US. These regulations may cover the emissions a product produces, the safety of the product, or how much interference the product causes to nearby devices. Depending on where a product is set to launch, it may need multiple device certifications from multiple different regulatory bodies.
Differing industries, such as medical, engineering, or telecommunications may have different regulations on associated devices to guarantee interoperability between devices. These regulations can include things such as standards for batteries, cybersecurity necessities, and over-the-air performance for wireless devices.
Cellular providers have their own mobile device certifications that wireless devices need to follow. Many carriers just enforce PTCRB, but many have their own in-house certifications. If your product is something that needs to be accepted by multiple carriers (such as a smartphones) you will need to be certified by each carrier that is available in the location you plan to launch your product in.
Many countries have regulations that are created by their government or by other lawmaking bodies, such as the FCC in the US. These regulations may cover the emissions a product produces, the safety of the product, or how much interference the product causes to nearby devices. Depending on where a product is set to launch, it may need multiple device certifications from multiple different regulatory bodies.
Differing industries, such as medical, engineering, or telecommunications may have different regulations on associated devices to guarantee interoperability between devices. These regulations can include things such as standards for batteries, cybersecurity necessities, and over-the-air performance for wireless devices.
Cellular providers have their own mobile device certifications that wireless devices need to follow. Many carriers just enforce PTCRB, but many have their own in-house certifications. If your product is something that needs to be accepted by multiple carriers (such as a smartphones) you will need to be certified by each carrier that is available in the location you plan to launch your product in.
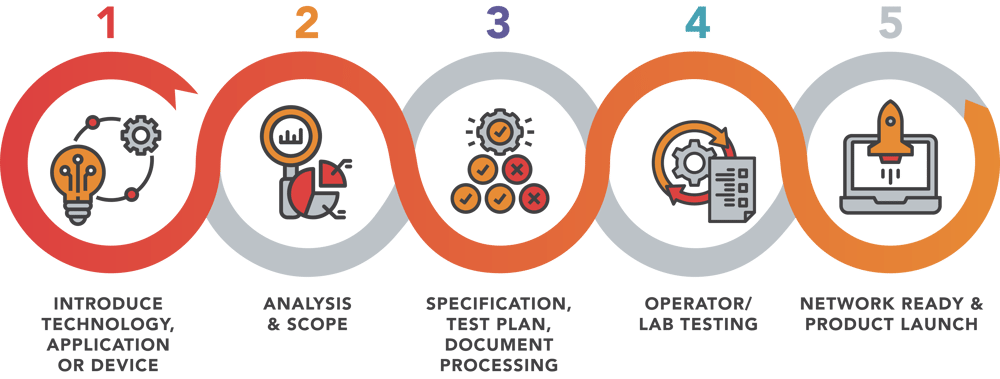
To ensure successful deployment of any IoT initiative, it’s imperative to find a partner with a proven track record of taking IoT devices through a streamlined accreditation process. KORE has a direct relationship with over a dozen of the world’s largest carriers and test labs, is an integral part of the certification ecosystem and has managed hundreds of customer device certifications.